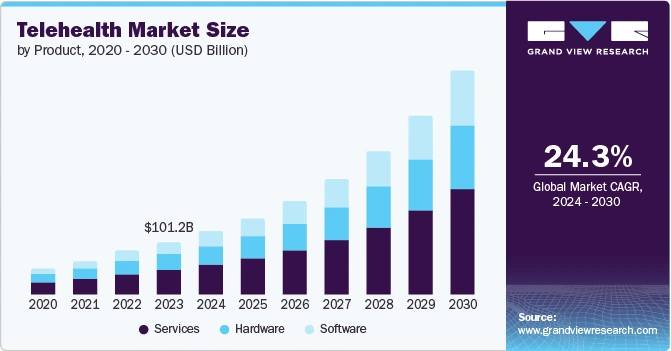
With almost 80% of hospitals now equipped with telehealth solutions, virtual care has become integral to modern healthcare delivery. Telehealth in primary care lets doctors conduct appointments through secure video calls, track patient health data remotely, and use digital tools to manage patient care. This approach helps providers to deliver timely care and avoid unnecessary hospital visits.
As healthcare needs evolve, implementing telehealth in primary care addresses key challenges, from providing care to rural communities to accommodating busy schedules. Telehealth PCPs (primary care providers) conduct routine check-ups, manage chronic conditions, and provide preventive care consultations—all through virtual platforms that adapt to patients’ schedules and locations.
To understand this growing shift in healthcare delivery, we explore what telehealth means in primary care, discuss the type of telehealth modalities available, and examine its benefits for both patients and health systems. We also address common challenges and show how different solutions can mitigate these issues.
What is Telehealth in Primary Care?
Telehealth in primary care is a healthcare delivery method where primary care doctors provide medical services through digital technology instead of traditional office visits. This includes diagnosis, treatment planning, patient monitoring, and follow-up care – all delivered through digital platforms
Telehealth PCPs deliver several types of care services:
- Virtual consultations for routine check-ups and minor illnesses through secure video calls
- Remote monitoring of ongoing health conditions using digital devices that track vital signs and symptoms
- Digital messaging for quick medical questions and prescription renewals
- Online screening systems that assess patient needs and guide them to appropriate care levels
Telemedicine in primary care works alongside traditional in-person care rather than replacing it completely. This hybrid approach particularly benefits patients in areas with limited access to secondary healthcare services. Studies also confirm that telehealth supports continuity of care, particularly for addressing minor health issues.
4 Types of Telehealth in Primary Care
Primary care providers use different types of telehealth methods to deliver patient care. These methods serve specific healthcare needs and offer distinct advantages:
1. Synchronous Telehealth (Real-Time Virtual Consultations)
Live video visits let physicians and patients communicate directly. During these appointments, doctors:
- Evaluate common illnesses and perform scheduled check-ups
- Monitor ongoing health conditions through regular discussions
Provide mental health support and prescription refills without requiring in-person visits.
This modality is particularly effective in reducing patient no-show rates, as studies indicate that telemedicine appointments are more likely to be completed.
2. Asynchronous Telehealth (Store-and-Forward Communication)
Asynchronous telehealth involves the exchange of medical data that providers can review at a later time. This model is useful for:
- Reviewing patient-submitted images (e.g., photos of skin conditions).
- Analyzing lab results or health histories.
- Offering follow-up advice when real-time consultation is not necessary.
This flexibility helps both patients and doctors manage their schedules effectively.
3. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) in Primary Care
Telehealth in primary care uses RPM to manage chronic diseases effectively. By tracking vital signs such as blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate via wearable devices or mobile apps, providers can intervene early and reduce complications. Notably, using RPM with biometrics has been associated with a 50% reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure.
4. Mobile Health (mHealth) Apps for Primary Care Patients
Current data shows that 43 percent of Americans use health apps in 2024. These apps help patients:
- Track medications and symptoms
- Manage health habits, including food and exercise
- Message their healthcare providers directly These tools help patients actively manage their health, making telemedicine in primary care more effective.
Telehealth in Primary Care for Patients
Telemedicine in primary care creates several advantages for patients. Let’s discuss how they benefit from digital healthcare:
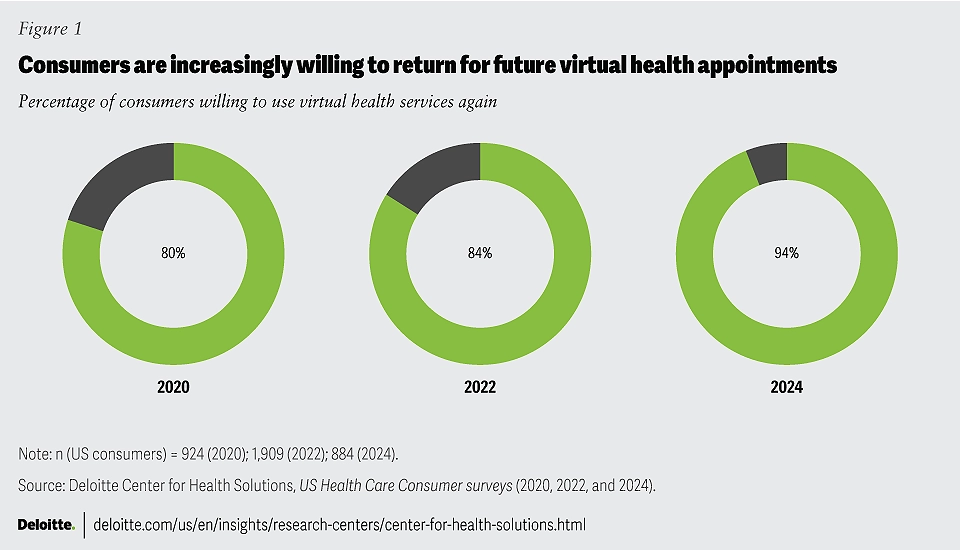
Better Access to Care
Telehealth in primary care helps more patients receive medical care, regardless of their location. This matters most for:
- Rural populations who live far from medical offices
- Elderly individuals or those with mobility issues.
- Patients who need regular check-ups for chronic health conditions.
Research also confirms that telehealth reduces travel time, cuts healthcare costs, and makes care easier to access, especially in rural communities.
Time and Convenience
Virtual consultations save time and reduce the need for commutes. This flexibility allows patients to:
- Schedule appointments that align with their personal and professional commitments.
- Access care quickly, reducing delays that could lead to complications.
- Benefit from shorter waiting times compared to traditional in-person visits.
This flexibility aligns perfectly with executive health benefits, which are designed to accommodate the demanding schedules of corporate leaders.
Improved Chronic Disease Management
Patients with conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease gain from regular monitoring through RPM. This approach:
- Enables doctors to respond quickly when readings change
- Helps patients take medications correctly
- Prevents hospital stays through early treatment
Remote monitoring tools show clear improvements in managing long-term health conditions. Research shows that telemonitoring offers care quality comparable to traditional in-person visits, with studies reporting lower death rates and better patient self-care. Patients also report high satisfaction with this care method.
Enhanced Mental Health Support
Telehealth makes mental health care easier to access by removing common barriers associated with stigma and travel. Online mental health visits:
- Help identify problems early
- Provide regular support for ongoing care
- Offer privacy and comfort, encouraging more patients to seek help
Studies show that virtual mental health care works as well as—and sometimes better than—in-person visits for treating many mental health conditions.
Lower Healthcare Costs for Patients
By reducing transportation expenses, lost work hours, and unnecessary emergency visits, telehealth PCPs lower the overall cost of care. Additional savings come from:
- Improved insurance reimbursement for virtual visits makes care more affordable.
- Preventive care through telehealth helps avoid costly hospitalizations.
Recent data shows that 24% of patients would change doctors to get virtual care, and 82% want more telehealth services when covered by insurance. This trend highlights the cost-saving potential of telehealth in primary care.
Greater Patient Engagement and Self-Management
Digital healthcare tools help patients take charge of their health. Through mobile health apps and remote monitoring devices, patients can:
- Stay in touch with their doctors
- Keep track of medications and symptoms
- Make healthy lifestyle changes
By fostering greater engagement, telehealth strengthens the patient-provider relationship and ensures personalized medical care tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Telehealth in Primary Care for Health Systems
Healthcare organizations gain multiple advantages when implementing telehealth in primary care, let’s discuss some of them:
Operational Efficiency and Optimized Workflows
Telehealth improves how healthcare providers handle daily operations. Digital tools streamline administrative work and help more patients attend their scheduled appointments. Healthcare organizations using virtual platforms achieve these improvements through:
- Automated scheduling systems that reduce staff workload and paperwork
- Smart appointment management that matches patients with available care providers
- Digital tools that help staff complete tasks more quickly and accurately
These operational improvements help health systems deliver better care while using their resources more effectively.
Expanded Patient Reach and Population Health Management
Telemedicine in primary care enables healthcare systems to serve more patients beyond their immediate locations. Healthcare organizations achieve this through:
- Remote monitoring of high-risk patients to prevent unnecessary hospital visits
- Better distribution of medical resources to underserved communities
- Continuous health monitoring that helps prevent serious complications
This approach reinforces care coordination initiatives and promotes equitable access to high-quality primary care.
Financial Benefits and Revenue Opportunities
Telehealth creates new revenue streams that help health systems maintain financial stability. While traditional practices explore virtual care options, the pros and cons of direct primary care models show how alternative payment structures can support sustainable telehealth implementation. The benefits include:
- Lower facility maintenance costs compared to traditional office visits
- Increased revenue from virtual consultations that complement in-person services.
- Better alignment with healthcare payment models that focus on preventive health
By tapping into these benefits of telemedicine, health systems can create sustainable models for ongoing care. Many organizations have found success by implementing executive health programs that combine comprehensive virtual care with preventive services for corporate clients.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Care Coordination
A telehealth platform that integrates with EHR systems enhances care coordination. Modern telehealth leverages the benefits of EHR through:
- Immediate access to patient health records
- Better communication between telehealth PCPs and specialists
- Automated data handling that reduces paperwork and mistakes
Better care coordination strengthens the overall quality of healthcare and supports efficient management of patient information.
Hybrid Care Models for Better Resource Allocation
A hybrid model that combines telehealth PCP services with traditional visits optimizes resource allocation. Minor conditions and routine follow-ups can be managed remotely, which:
- Frees up clinical space for urgent and complex cases.
- Reduces provider burnout by balancing workloads.
- Enhances patient flow and overall clinic efficiency.
Enhancing Healthcare System Resilience
Telehealth strengthens healthcare systems during crises like pandemics or natural disasters. virtual healthcare platforms allow health systems to:
- Handle non-urgent medical needs remotely to prevent hospital overcrowding
- Continue providing essential care when physical access is limited
- Support emergency response and recovery through digital health monitoring
- Manage travel-related health risks by offering remote consultations before, during, and after travel
These digital capabilities help telehealth PCPs maintain consistent care delivery even in challenging situations.
Challenges of Telehealth in Primary Care
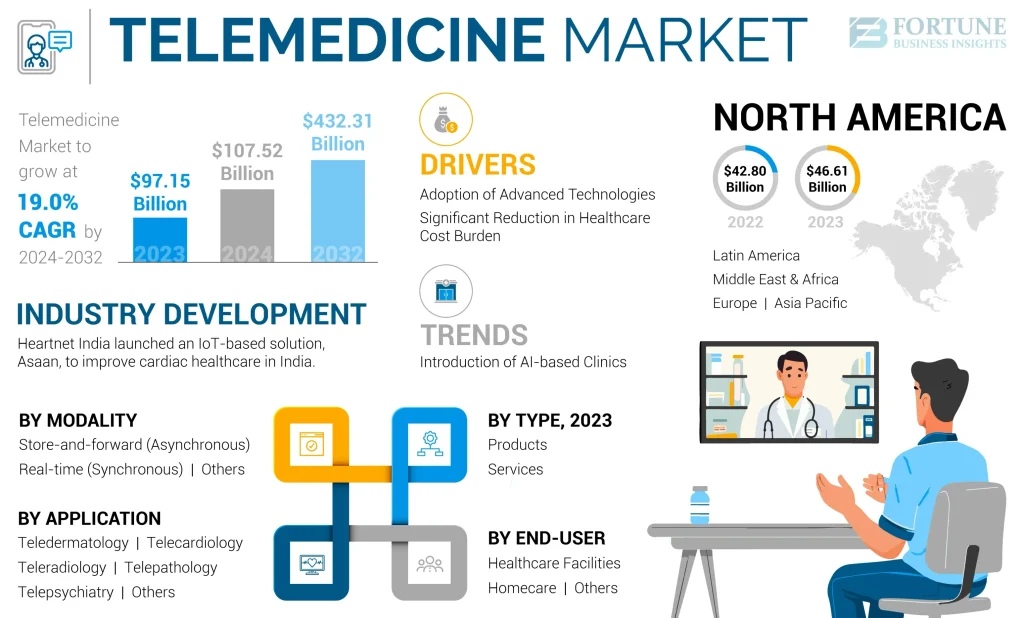
While the benefits are clear, certain challenges can impact the adoption of telehealth in primary care. Understanding and addressing these obstacles helps ensure successful implementation.
1. Technological Barriers
Limited technology access affects how patients and providers use telemedicine in primary care. Common issues include:
- Poor internet connections that interrupt virtual appointments
- Outdated devices that don’t support video calls
- Difficulty using digital healthcare platforms
WorldClinic addresses these issues by using secure, user-friendly platforms designed for accessibility—even in remote areas. Their concierge model offers personalized support and hands-on assistance to ensure a smooth telehealth experience.
2. Regulatory and Licensing Issues
Healthcare regulations and licensing requirements create significant challenges for implementing telehealth in primary care across different locations. Each state maintains its own rules about how doctors can provide virtual care, affecting everything from prescribing medications to maintaining patient records.
Telehealth PCPs need clear procedures to handle these regulatory differences. They must regularly update their knowledge of state regulations, maintain appropriate licenses, and adjust their virtual care practices to meet local requirements.
3. Reimbursement Complexities
Insurance coverage for virtual healthcare visits varies significantly among providers. Telehealth PCPs face uncertainty about payment rates and coverage limits for digital services. Some insurance companies limit the types of virtual visits they cover, while others set different payment rates for in-person and virtual care.
These payment variations affect healthcare providers in several ways:
- Unpredictable revenue from virtual visits
- Extra staff time spent verifying insurance coverage
- Complex billing procedures for virtual services
- Difficulty planning long-term virtual care programs
Membership-based care models offer an alternative approach to traditional insurance billing. Membership medicine offers 24/7 access to virtual care services through direct payment arrangements between patients and healthcare providers, without traditional insurance reimbursements.
4. Patient Digital Literacy
Another challenge of telehealth is e-health literacy, as some patients, particularly older adults or those less familiar with technology, may struggle with telemedicine platforms. This can result in missed appointments or reluctance to adopt virtual care. WorldClinic prioritizes user-friendly and intuitive telehealth solutions, supported by a guided approach, to ensure that patients of all digital literacy levels can access care with ease.
5. Security and Privacy Concerns
Protecting patient data remains a critical challenge as healthcare moves into digital spaces. Telehealth in primary care involves transmitting sensitive medical information through virtual platforms, creating new security responsibilities for healthcare providers:
- Patient data protection during virtual appointments
- Safe storage of digital health records
- Prevention of unauthorized access to medical information
- Compliance with healthcare privacy regulations
WorldClinic mitigates these risks by implementing stringent security measures, encrypted medical record integrations, and HIPAA-compliant telehealth solutions to ensure the confidentiality and safety of patient data.
Conclusion
Telehealth in primary care continues to transform healthcare delivery through improved access, efficiency, and patient care. Through secure video visits, health monitoring, and digital communication tools, healthcare providers deliver more responsive care that meets patient needs. This approach reduces travel time for patients, lowers healthcare costs, and helps doctors manage ongoing health conditions more effectively.
Healthcare organizations implementing telemedicine in primary care see clear benefits in their operations. Telehealth PCPs reach more patients, work more efficiently, and maintain stable services despite common challenges. While issues like technology access, regulations, and insurance coverage exist, healthcare organizations continue to develop effective solutions.
As we look to the future, implementing telehealth in primary care will remain essential for delivering quality healthcare. Modern healthcare delivery increasingly demonstrates that concierge primary care practices excel at integrating telehealth solutions, providing patients with superior virtual care experiences, while maintaining personalized attention.
Want to learn how telehealth can improve care experience? Explore WorldClinic’s concierge medical services and discover how our personalized approach can meet your healthcare needs.
Experience Personalized Healthcare Anywhere, Anytime
Discover how WorldClinic’s Concierge Telemedicine Services put world-class medical expertise at your fingertips. From 24/7 access to tailored medical solutions, our memberships ensure peace of mind and proactive care for you and your family.
FAQ About Telehealth In Primary Care
1. What types of medical conditions can be treated via telehealth?
Telehealth primary care providers can treat non-emergency medical needs. Doctors can manage common illnesses, conduct regular check-ups, monitor ongoing conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, and provide mental health care through video appointments.
2. How do primary healthcare providers ensure data security in telehealth services?
Primary healthcare providers use secure, encrypted telehealth systems that follow strict medical privacy laws. These digital platforms protect patient information during virtual appointments and when medical records are shared between healthcare providers.
3. How does telehealth support preventive care and routine screenings?
Primary care doctors use telehealth for preventive care, through online appointments and remote monitoring. They catch potential health issues early and help patients avoid emergency visits.
4. Can telehealth be used for emergency medical situations?
No, telehealth is designed for non-emergency care. Patients with urgent medical needs should go to emergency rooms or call emergency services. Virtual care helps by handling routine visits, which leaves emergency rooms free for critical cases. Learn more about the difference between urgent care and primary care for further clarification.
5. How does telehealth improve care coordination between primary care providers and specialists?
Integration with interoperable electronic health records (EHR) and dedicated care coordination systems allows providers to share patient data seamlessly. This integration improves clinical decision-making and supports collaborative care across different specialties.


